Arete - automated testing service¶
Arete automated testing system consists of four microservices, each has a clearly defined task.
Services¶
Monitoring service¶
Provides statistical insights into the usage of the testing system. For example, you can view test success rates, submission frequency, and system statistics. The application is built with Vue 2
Source code is in gitlab.
Automated Testing Service¶
Handles the launch of code testing. Responsible for receiving test requests, adding work to the RabbitMQ queue, waiting for results and later, storing and forwarding results to the specified return url. The service is developed using the Java Spring Boot framework and runs in a self-contained Docker container
Source code is in gitlab.
Authentication Service¶
Checks the validity of incoming test requests and is responsible for securely forwarding requests to the Automated Testing Service. Also implemented using Spring Boot and containerized in a Docker environment
Source code is in gitlab.
Test Runners¶
Runs the code testing. Receives work from RabbitMQ, launches a language-specific tester (Python, Java, C++, F#...etc) in a separate Docker container, when it finishes, it reads the test results, and sends them back to the Automated Testing Service via RabbitMQ. The service itself is developed with SpringBoot and also runs containerized.
There can be multiple Test Runners connecting to the same RabbitMQ queue, that is for load balancing. Because each testing usually takes around 5 to 10 seconds, the more Test Runners there are, the faster the system usually is, especially on exams. Each test runner can also be configured from monitoring service, how much testings it can run in parallel.
Source code is in gitlab.
How the testing works¶
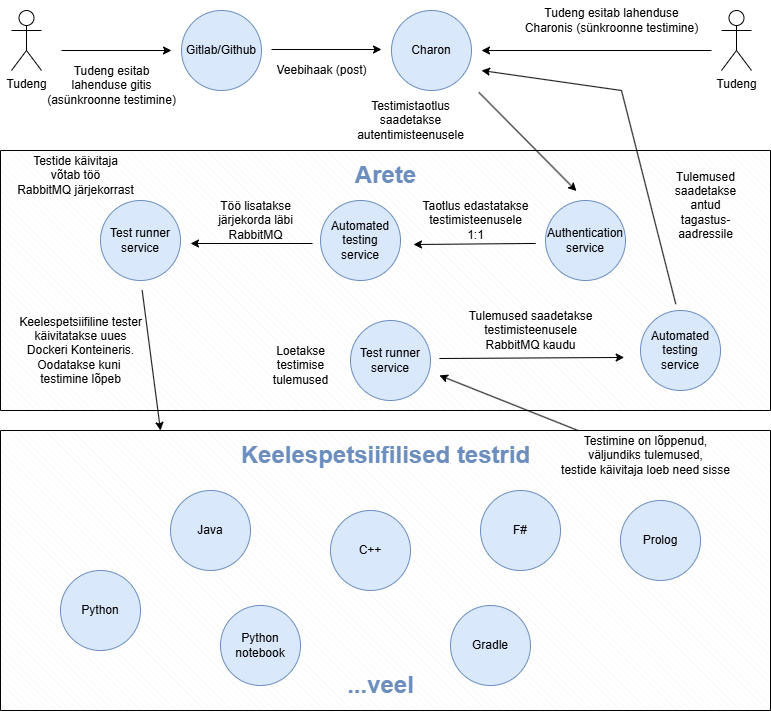
The automated testing system enables efficient and scalable assessment of programming assignments submitted by students using a microservices-based architecture. The central component of the system is Arete, which mediates testing requests and coordinates their execution. A system called Charon is used to aggregate and assess the results. There are two possible ways for students to start testing:
Submitting via Git (asynchronous testing) - Student submits their solution to a Github or Gitlab repository. This triggers an event via a webhook, which is forwarded to Charon. Charon identifies the task and forwards the testing request to the Arete environment. Authentication takes place there, after which the request is moved to a message queue (RabbitMQ) via the testing service.
Submitting inline via Charon (synchronous testing) - Student can also submit their solution directly through the Charon web interface. In this case, a synchronous query is made, the result of which is returned directly to the user after testing is complete. This allows the student to get faster feedback without the mediation of Git.
In both cases, the test request is moved to the Arete environment, the Automated Testing Service adds the job to the RabbitMQ queue, the Test Runner Service takes the job from the queue and launches the corresponding language tester in a special Docker container. Language-specific testers (e.g. Python, Java, C++, Prolog, Gradle, etc.) perform automatic testing of the solution, after which the results are saved and returned to the Test Runner Service.
The results are sent back to Automated Testing Service via RabbitMQ, and then forwarded to the Charon (or any other specified return url), where they are stored and made available to both the student and the teacher. Charon plays an important role: it is not only a test results management system, but also allows for grading and visual display of the results.